Product Pricing Strategies are essential in business for maximizing profit and satisfying customers. From cost-based to value-based pricing, each strategy plays a crucial role in consumer behavior and purchasing decisions. Let’s dive into the world of pricing strategies and explore how businesses can thrive in the competitive market landscape.
Overview of Product Pricing Strategies
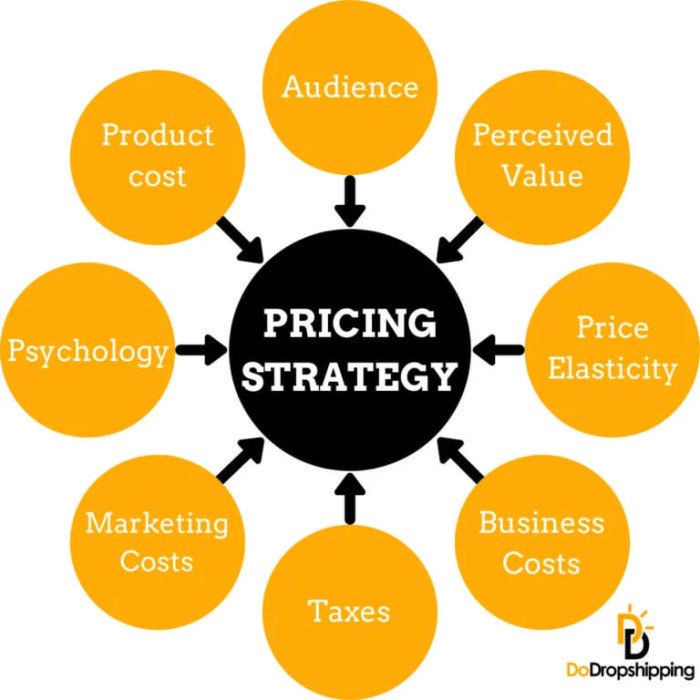
Product pricing strategies are essential in business as they determine the value of a product in the market, influence consumer behavior, and impact purchasing decisions. By setting the right price, businesses can maximize profits, increase market share, and maintain a competitive edge.
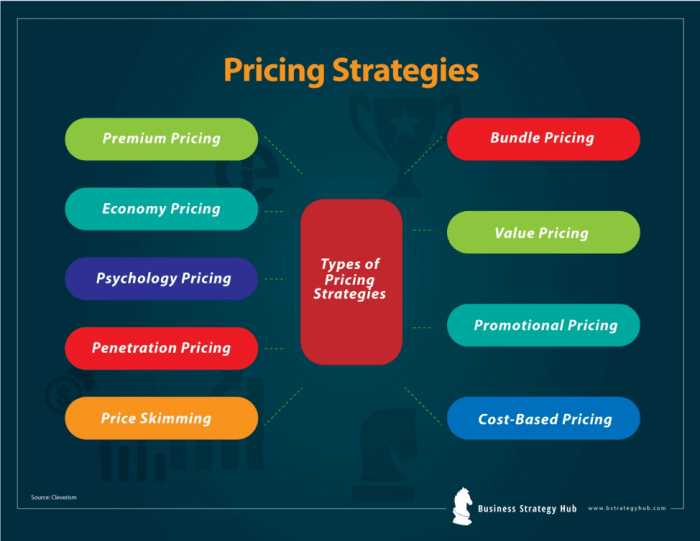
Types of Product Pricing Strategies
- Penetration Pricing: Setting a low price to enter the market and attract customers.
- Price Skimming: Setting a high price initially to target early adopters and recoup development costs.
- Competitive Pricing: Pricing products based on competitors’ prices to stay competitive in the market.
- Value-Based Pricing: Setting prices based on the perceived value of the product to customers.
- Bundle Pricing: Offering discounts when customers buy multiple products together.
Impact of Product Pricing Strategies on Consumer Behavior
Product pricing strategies play a significant role in influencing consumer behavior and purchasing decisions. Consumers often associate higher prices with better quality products, leading to a perception of value. On the other hand, lower prices may attract price-sensitive customers but could also create a perception of inferior quality. By understanding consumer psychology and preferences, businesses can strategically set prices to drive sales and build brand loyalty.
Cost-Based Pricing
Cost-based pricing is a strategy where prices are determined by considering the production cost, including materials, labor, and overhead expenses, and adding a markup to ensure a profit margin. This method focuses on covering costs and generating a desired level of profit.
Components of Cost-Based Pricing
- Variable Costs: These are costs that vary with the level of production, such as raw materials and direct labor.
- Fixed Costs: These are costs that remain constant regardless of the level of production, such as rent and salaries.
- Markup: The amount added to the total cost to determine the selling price and profit margin.
Advantages of Cost-Based Pricing
- Simple and easy to calculate, making it straightforward for businesses to set prices.
- Ensures that all costs are covered, preventing losses from underpricing.
- Provides a predictable profit margin, helping with financial planning and stability.
Disadvantages of Cost-Based Pricing
- Does not consider customer demand or market conditions, potentially leading to missed opportunities for higher prices.
- May not account for competition, resulting in pricing that is not competitive in the market.
- Risks undervaluing products if costs are miscalculated or underestimated.
Real-World Example
One company that uses cost-based pricing is Apple Inc. When determining the prices for their iPhones, Apple considers the costs of production, including materials and labor, and adds a markup to ensure profitability. This approach allows Apple to maintain premium pricing for their products while covering all expenses and generating a profit.
Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing is a strategy where companies set prices based on the perceived value of their products or services to customers, rather than solely considering the cost of production. This approach focuses on what customers are willing to pay for a particular product or service, taking into account factors such as quality, brand reputation, and unique features.
Benefits of Value-Based Pricing
- Maximizes profits: By aligning prices with the perceived value, companies can capture a larger share of the value they create for customers.
- Competitive advantage: Value-based pricing allows companies to differentiate themselves from competitors based on the unique value they offer, rather than engaging in price wars.
- Customer satisfaction: When customers perceive that they are getting good value for the price they pay, they are more likely to be satisfied with their purchase and become loyal repeat customers.
Determining Perceived Value
Determining the perceived value of a product involves understanding the needs, preferences, and perceptions of customers. Companies can use market research, customer surveys, focus groups, and competitor analysis to gather data on how customers perceive the value of their products compared to alternatives in the market. By analyzing this information, companies can set prices that reflect the value customers place on their offerings, ultimately leading to higher profitability and customer satisfaction.
Competitor-Based Pricing
Competitor-based pricing is a strategy where companies set their prices based on what their competitors are charging for similar products or services. This approach involves monitoring the pricing strategies of competitors and adjusting prices accordingly to stay competitive in the market.
Significance of Competitor-Based Pricing
- Helps companies stay competitive: By keeping an eye on competitor pricing, companies can ensure that their prices are in line with what customers are willing to pay.
- Allows for quick adjustments: Companies can react swiftly to price changes by competitors, helping them maintain market share.
- Provides valuable market insights: Monitoring competitor pricing can offer insights into market trends and customer preferences.
Examples of Companies Adjusting Pricing Based on Competitors, Product Pricing Strategies
- Apple vs. Samsung: Both tech giants often adjust the pricing of their smartphones based on each other’s releases to stay competitive in the market.
- Coca-Cola vs. Pepsi: These beverage companies frequently monitor each other’s pricing strategies to ensure they remain competitive in the soft drink industry.
Risks Associated with Competitor-Based Pricing
- Price wars: Constantly adjusting prices based on competitors can lead to price wars, resulting in lower profit margins for all companies involved.
- Loss of brand value: Setting prices solely based on competitors can undermine a company’s brand value and positioning in the market.
- Limited differentiation: Companies may struggle to differentiate their products or services if they are solely focused on matching competitor prices.